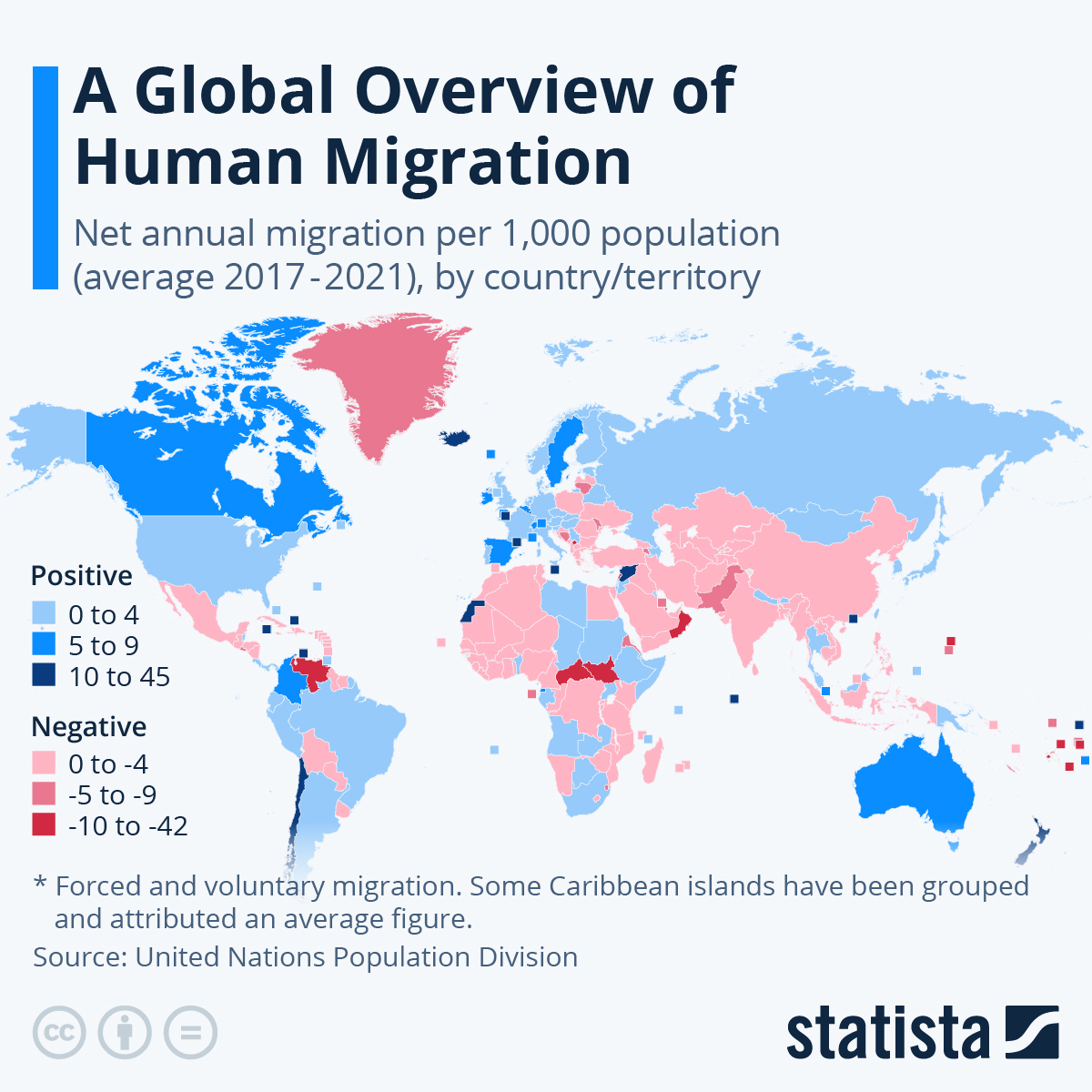

Migration has always been a defining feature of human history. From ancient trade routes to modern labor markets, people have moved across regions in search of safety, opportunity, and a better quality of life. In the 21st century, however, global migration has become more complex, large-scale, and politically sensitive than ever before.
According to international estimates, hundreds of millions of people today live outside their country of birth, making migration a central issue for governments, economies, and societies worldwide. This blog explores the latest global migration trends, their root causes, and the economic, social, and political consequences they create.
📊 Understanding Global Migration Today
Migration broadly refers to the movement of people from one place to another, either within a country (internal migration) or across national borders (international migration). This blog focuses mainly on international migration, which includes:
Economic migrants (seeking jobs and better income)
Refugees and asylum seekers (fleeing war, persecution, or violence)
Students and skilled professionals
Climate and disaster-displaced populations
Organizations such as the United Nations, International Organization for Migration, and UNHCR track and analyze these movements globally.
🌐 1. Major Global Migration Trends

🔹 Rising International Migration
The number of international migrants has steadily increased over the last few decades. Migration today is more globalized, with people moving not only from poorer to richer countries, but also between developing nations (South-South migration).
🔹 Growth of Forced Migration
Conflicts, political instability, and human rights violations have led to a sharp rise in refugees and internally displaced persons (IDPs). Regions affected by war and unrest have become major sources of forced migration.
🔹 Skilled & Student Migration
Highly skilled workers, doctors, engineers, and IT professionals are increasingly migrating to countries facing labor shortages. International student mobility has also expanded, linking education with long-term migration.
🔹 Urban-Centered Migration
Migrants increasingly settle in large cities, making urban areas hubs of cultural diversity but also putting pressure on housing, infrastructure, and services.
⚙️ 2. Causes of Global Migration
Migration is rarely driven by a single factor. Instead, it results from a combination of push and pull forces.
🧭 A. Economic Causes


Lack of employment opportunities in home countries
Low wages and poverty
Demand for labor in developed economies
Higher living standards and career growth abroad
💰 Remittances, money sent home by migrants, play a crucial role in supporting families and national economies in many developing countries.
⚔️ B. Political Conflict and Insecurity
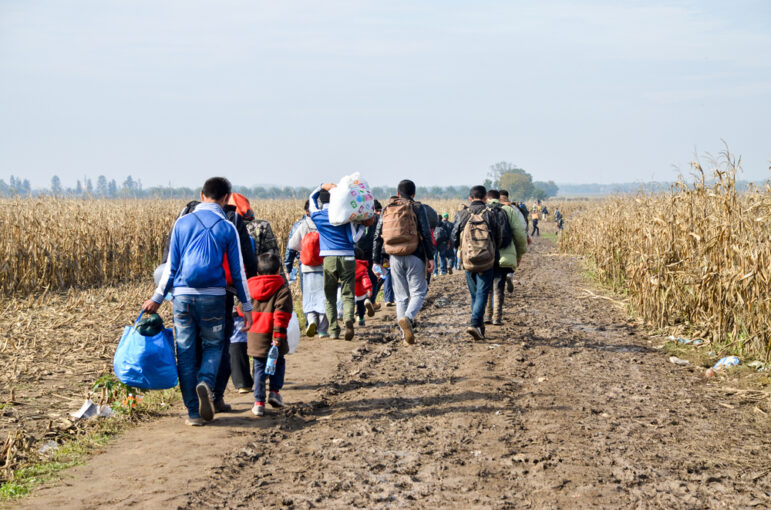
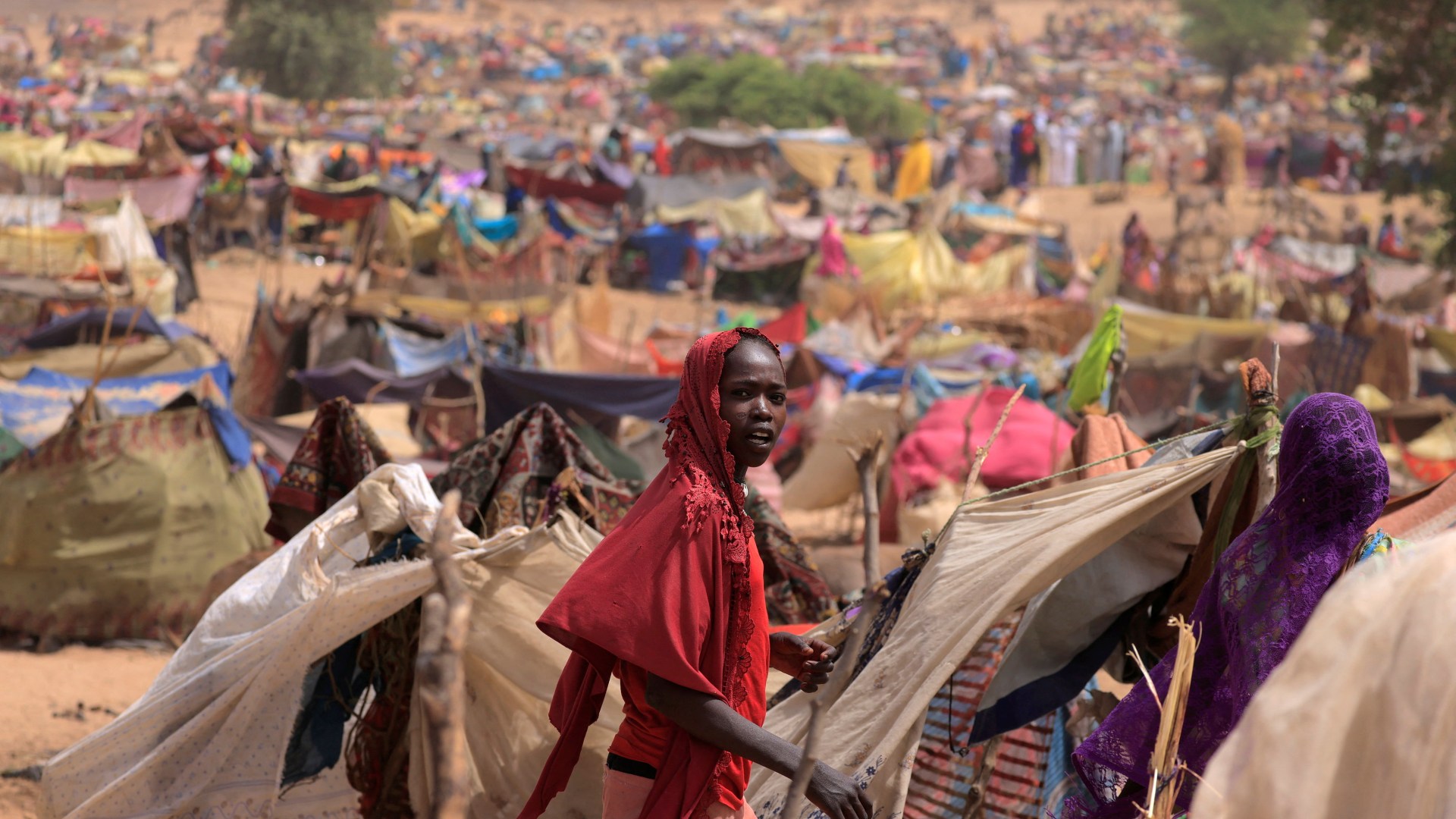
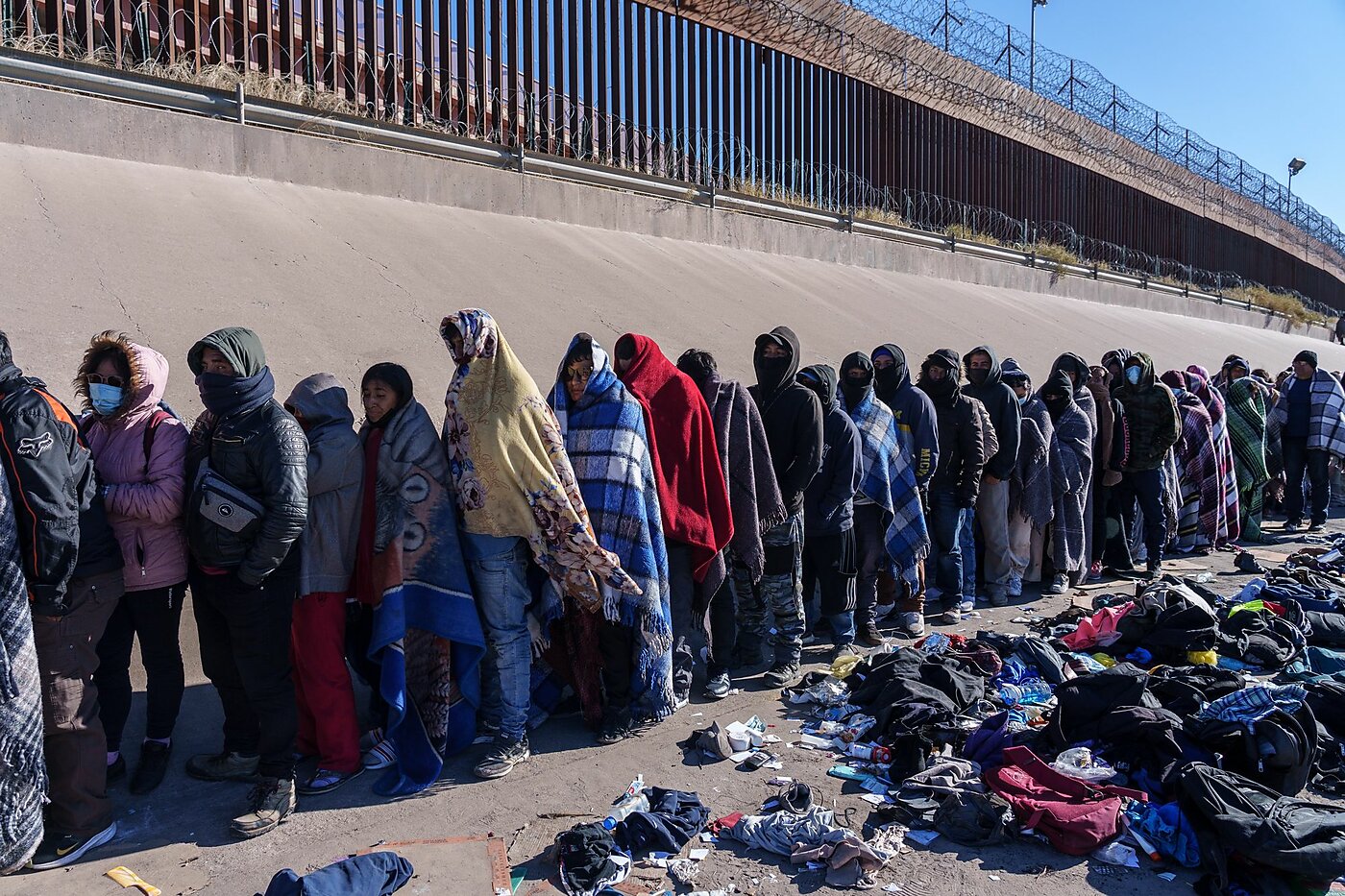



Armed conflicts and civil wars
Political persecution and authoritarian regimes
Ethnic, religious, or ideological violence
Millions are forced to flee their homes to save their lives, often with little planning or resources.
🌡️ C. Climate Change and Environmental Factors



Climate change is emerging as a major driver of migration:
Rising sea levels threatening coastal communities
Droughts affecting agriculture and livelihoods
Extreme weather events (floods, cyclones, heatwaves)
🌍 These migrants are often called climate migrants, though international law has yet to fully recognize them as refugees.
🎓 D. Education and Social Factors
Access to quality education
Family reunification
Healthcare and social security
Desire for personal freedom and better social conditions
🌍 3. Consequences of Global Migration
Migration produces both positive and negative impacts, affecting origin countries, destination countries, and migrants themselves.
💹 A. Economic Consequences
✔️ Positive Impacts
Fills labor shortages in destination countries
Boosts productivity and innovation
Migrants contribute taxes and social security
Remittances support development in origin countries
❌ Challenges
Brain drain from developing countries
Pressure on wages in low-skill sectors
Unequal access to economic opportunities
🧑🤝🧑 B. Social and Cultural Consequences


✔️ Positive Effects
Cultural diversity and exchange
Enrichment of food, language, arts, and ideas
More open and globalized societies
❌ Challenges
Integration difficulties
Language and identity barriers
Rise of xenophobia and discrimination
Social tensions in host communities
🏛️ C. Political and Policy Impacts
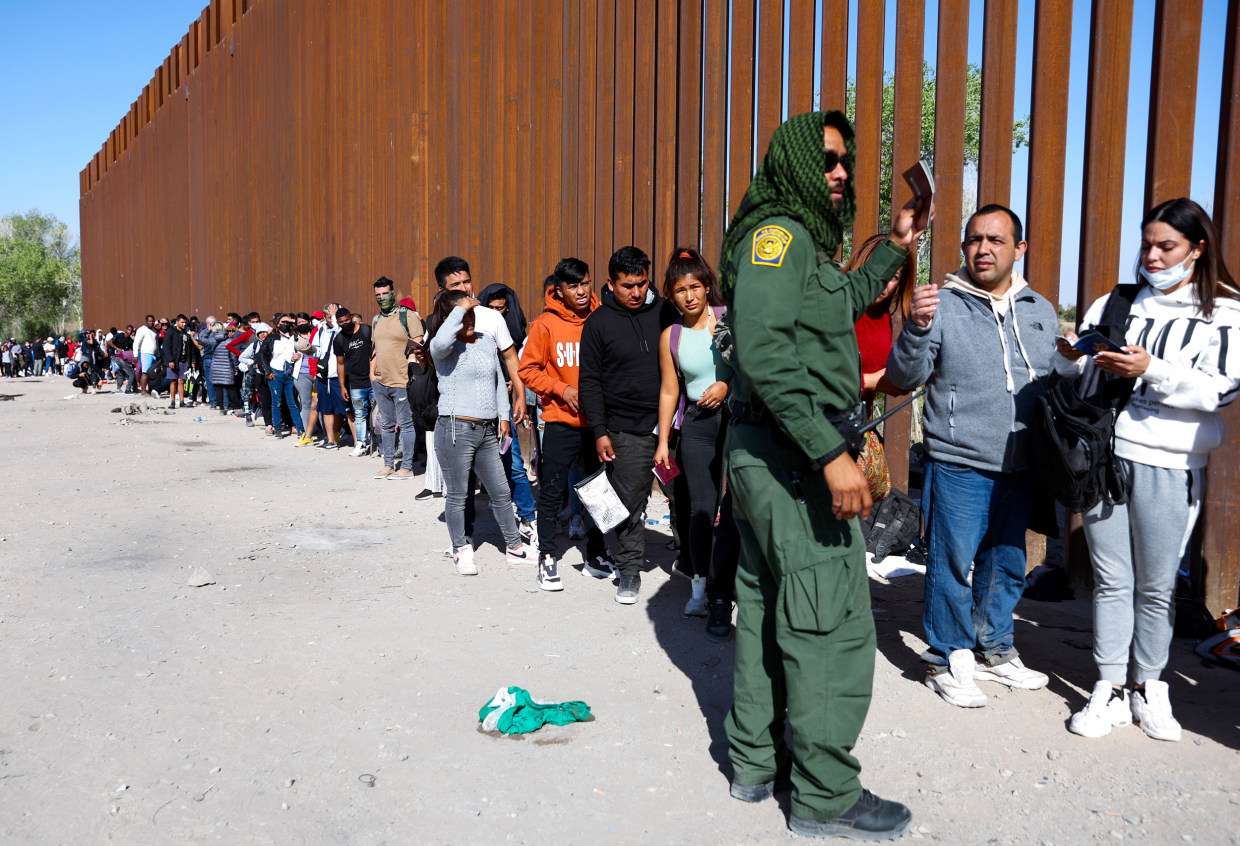



Migration has become a major political issue:
Debates over border control and national security
Strain on asylum systems
Rise of anti-immigration movements
Need for international cooperation
Governments struggle to balance humanitarian responsibility with domestic political pressures.
🧠 D. Human and Psychological Consequences
For migrants themselves:
Trauma from conflict or displacement
Separation from family and homeland
Identity struggles and mental health challenges
Risk of exploitation and unsafe working conditions
Yet migration can also mean hope, resilience, and new beginnings.
🔮 4. The Future of Global Migration
Experts agree that migration will continue to grow, driven by:
Climate change
Global inequality
Aging populations in developed countries
Technological and economic shifts
Future migration management will require:
Strong international cooperation
Legal migration pathways
Protection of migrant rights
Integration-focused policies
Organizations like the International Organization for Migration emphasize that migration, if well-managed, can be a powerful force for development rather than a crisis.
✅ Conclusion
Global migration is one of the most defining challenges and opportunities of our time. It reflects deep inequalities, conflicts, and environmental pressures — but also human ambition, adaptability, and resilience.
Rather than viewing migration solely as a problem, the global community must recognize it as a shared responsibility that requires compassion, cooperation, and smart policy.
🌍 Migration is not just about moving people — it is about shaping the future of societies worldwide.


