How Climate Change is Reshaping Global Landscapes



Introduction
Climate change is no longer a distant environmental issue—it is a visible force reshaping Earth’s landscapes in real time. From melting glaciers and rising seas to expanding deserts and shifting forests, the physical face of our planet is changing faster than at any point in recorded history.
Driven mainly by rising global temperatures, altered rainfall patterns, and extreme weather events, climate change is transforming natural ecosystems, human settlements, and geographical boundaries. This blog explores how climate change is reshaping global landscapes, the regions most affected, and what these changes mean for humanity’s future.
Understanding Climate Change and Landscapes
A landscape includes landforms, ecosystems, coastlines, rivers, glaciers, forests, and human-modified environments. Climate change affects landscapes by altering:
Temperature patterns
Precipitation and water cycles
Sea levels
Soil quality and vegetation
Frequency of extreme events
Scientific assessments by organizations like the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) confirm that human activities—especially fossil fuel use and deforestation—are the dominant cause of recent climate change.
1. Melting Glaciers and Polar Transformation


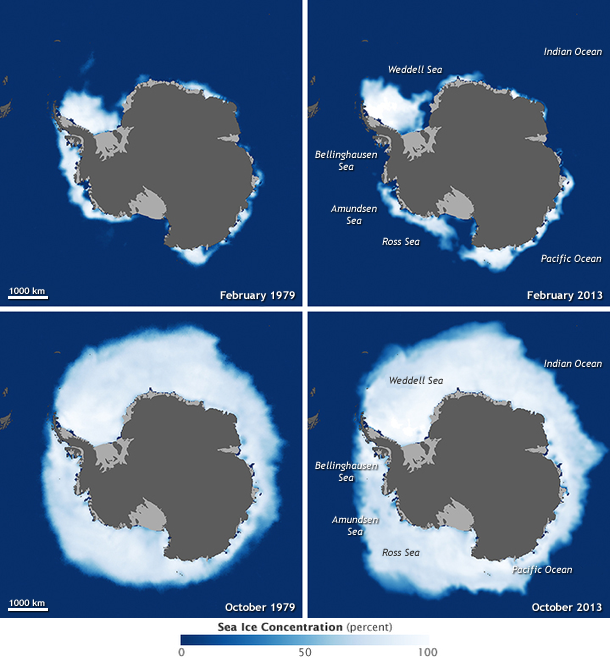
What’s Happening?
Rising temperatures are causing glaciers and ice sheets to melt at alarming rates.
Global Impact:
Himalayan glaciers shrinking, threatening water supply for millions
Arctic sea ice loss reducing natural cooling of the planet
Antarctic ice melt contributing to global sea-level rise
Landscape Change:
Formation of new glacial lakes
Increased risk of floods and landslides
Permanent loss of ice-dominated landscapes
According to National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), polar ice loss is accelerating faster than earlier predictions.
2. Rising Sea Levels and Coastal Erosion
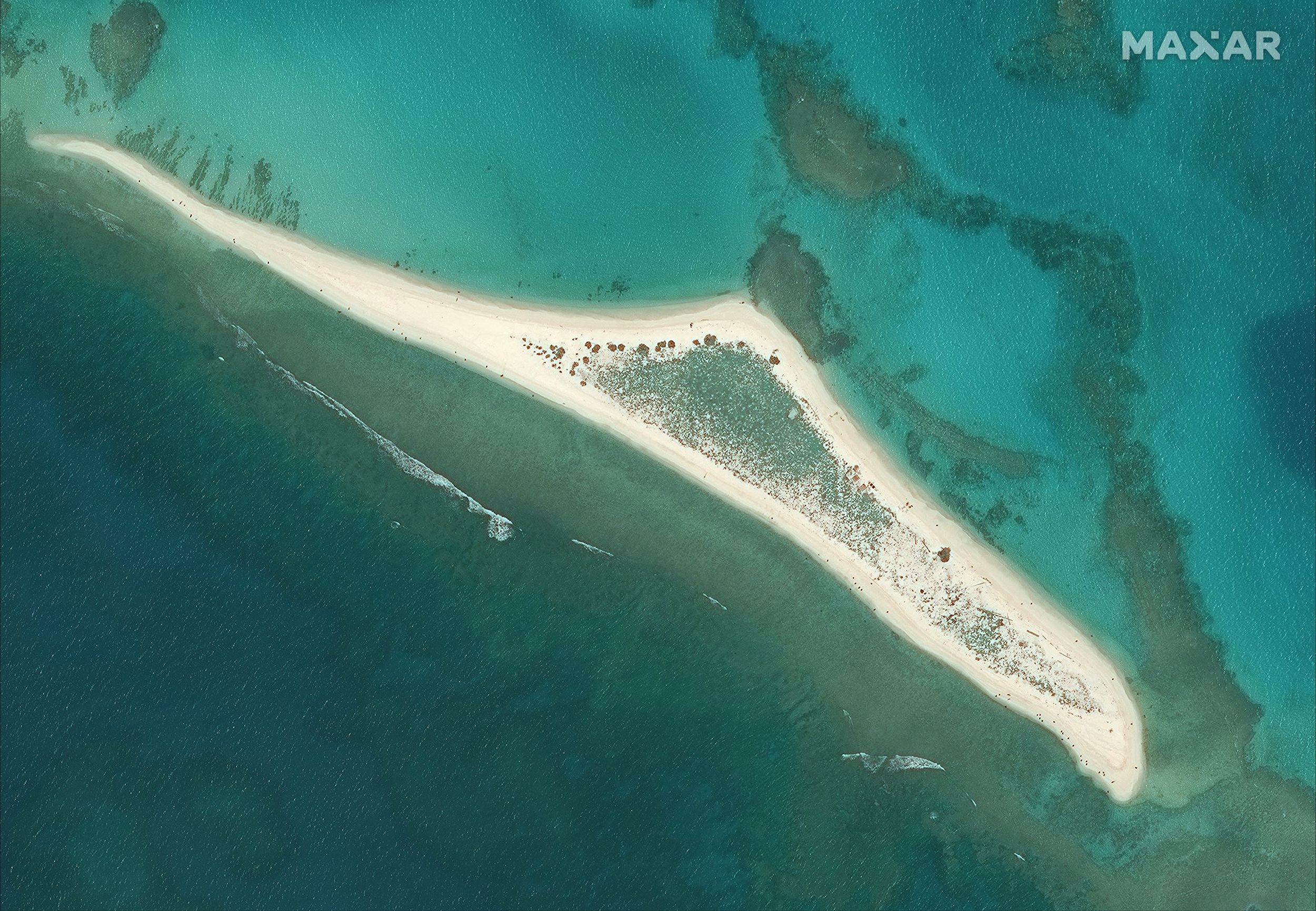



What’s Happening?
Melting ice and thermal expansion of seawater are causing global sea levels to rise.
Affected Landscapes:
Low-lying islands and deltas
Coastal cities and beaches
Mangroves and wetlands
Consequences:
Submerged land and disappearing shorelines
Saltwater intrusion into freshwater sources
Forced migration of coastal communities
Some island nations face the possibility of complete physical disappearance, redefining the concept of national borders.
3. Desertification and Land Degradation
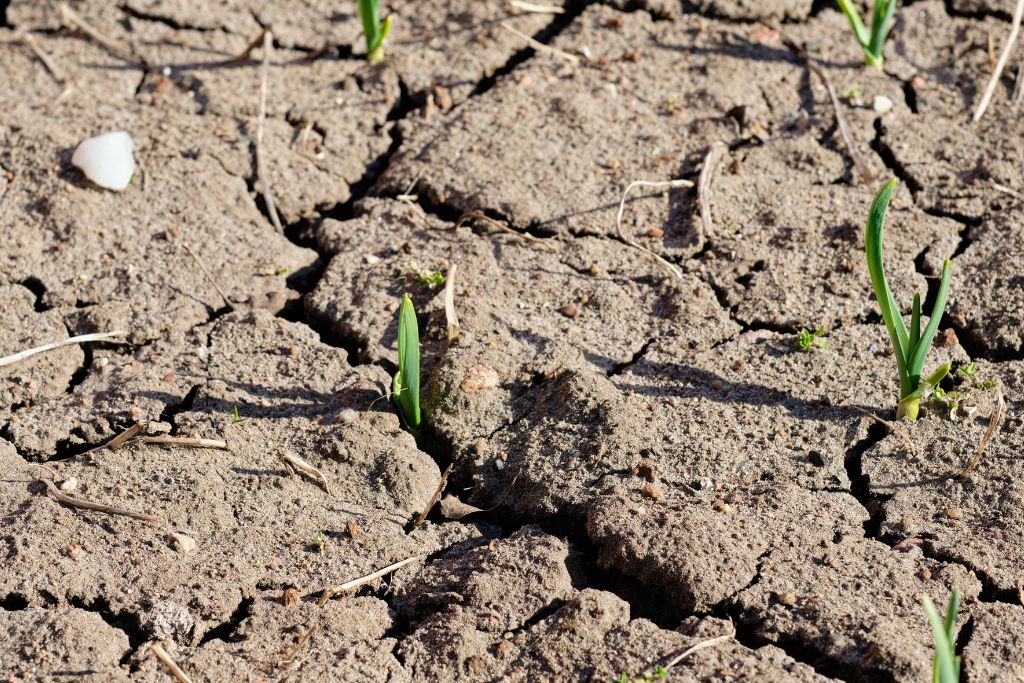

 What’s Happening?
What’s Happening?Rising temperatures and reduced rainfall are turning fertile land into desert-like terrain.
Regions at Risk:
Sub-Saharan Africa
South Asia
Middle East
Landscape Effects:
Loss of vegetation
Soil erosion and reduced fertility
Shrinking agricultural land
Desertification alters not just geography, but livelihoods, increasing poverty and climate-driven migration.
4. Forests Under Stress and Transformation
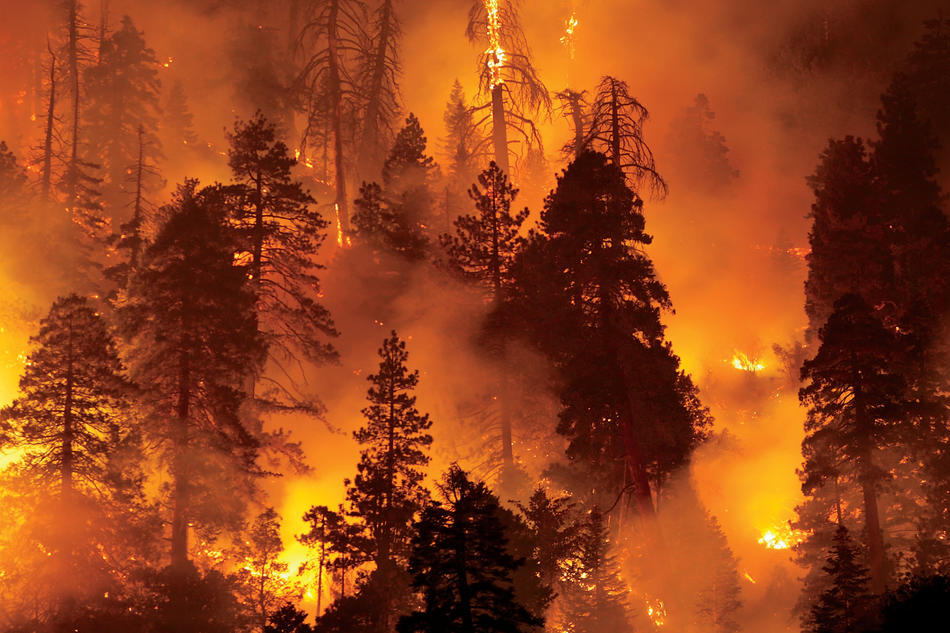
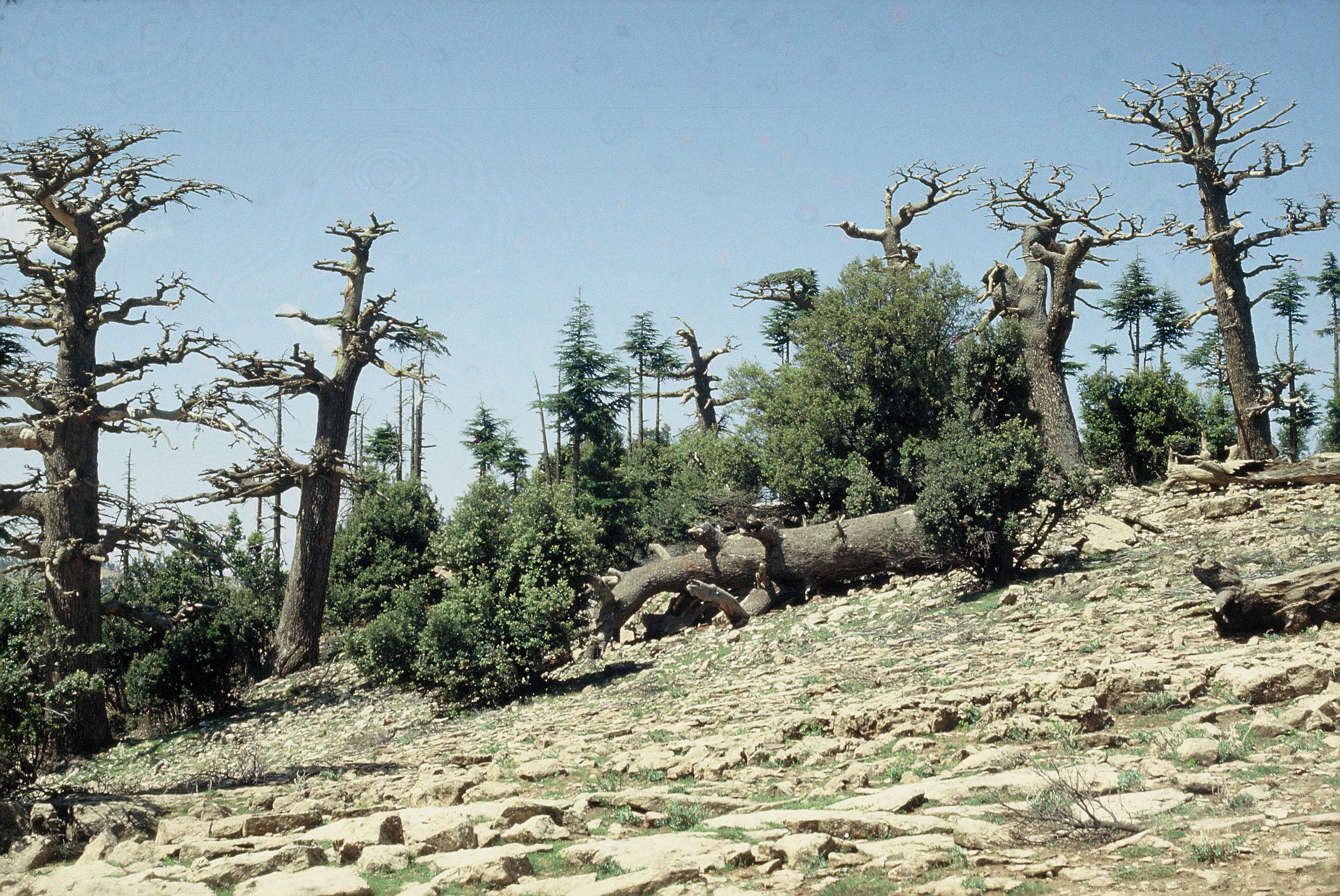



What’s Happening?
Climate stress combined with deforestation is reshaping forest ecosystems.
Key Changes:
Increased wildfires
Tree species migration to cooler regions
Forest dieback due to drought and pests
Example:
The Amazon rainforest, often called the “lungs of the Earth,” is shifting from a carbon sink to a carbon source in some areas—dramatically altering its ecological role.
5. Changing River Systems and Water Landscapes



What’s Happening?
Climate change disrupts the global water cycle.
Effects on Landscapes:
Drying rivers and lakes
Unpredictable flooding
Altered river courses
Impact:
Reduced freshwater availability
Damage to wetlands and floodplains
Increased conflicts over water resources
6. Urban Landscapes and Climate Pressure
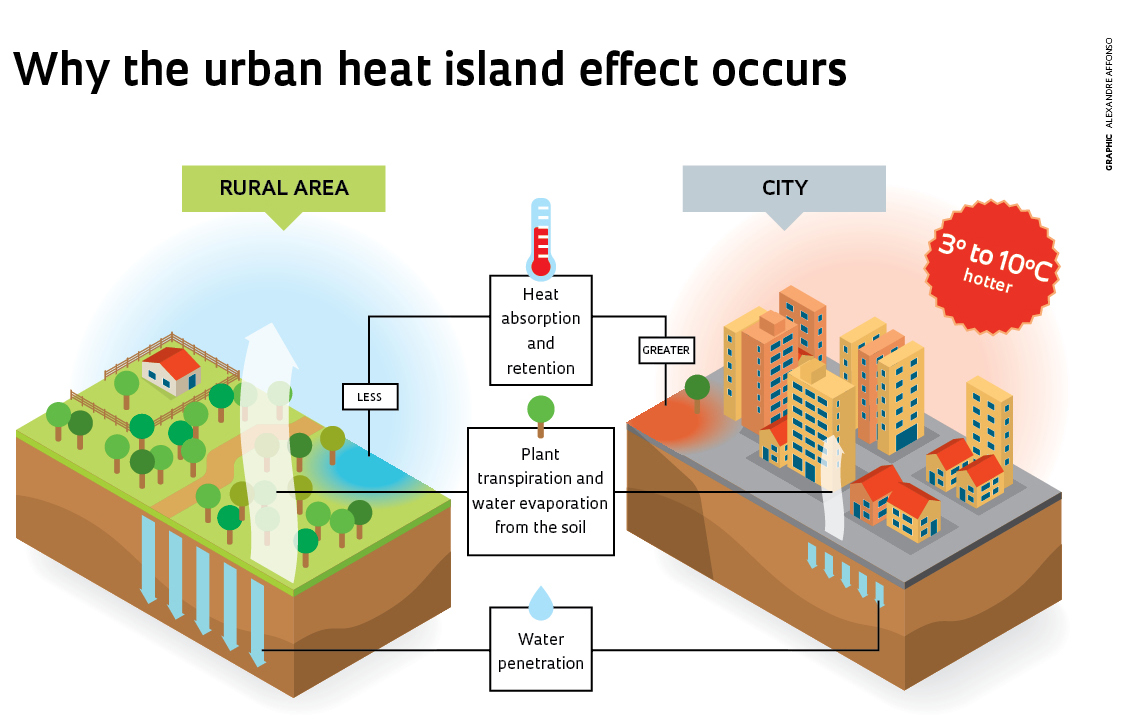

Cities are also landscapes—and climate change is reshaping them too.
Urban Changes:
Rising temperatures (urban heat islands)
Flooded infrastructure
Increased demand for climate-resilient design
Future cities must adapt with green spaces, climate-smart planning, and resilient infrastructure.
Human Consequences of Landscape Change
When landscapes change, human life changes with them:
Displacement and climate migration
Food and water insecurity
Economic instability
Loss of cultural and natural heritage
Landscape transformation is not just environmental—it is social, economic, and political.
Can These Changes Be Slowed or Managed?
Mitigation:
Reducing greenhouse gas emissions
Transitioning to renewable energy
Protecting forests and oceans
Adaptation:
Climate-resilient agriculture
Coastal protection and restoration
Sustainable land and water management
International cooperation guided by scientific research remains critical.
The Future of Global Landscapes
If current trends continue:
Ice-dominated regions will shrink further
Coastlines will retreat inland
Drylands will expand
Ecosystems will reorganize
However, human choices today will shape tomorrow’s landscapes. The future is not yet fixed.
Conclusion
Climate change is actively redrawing the physical map of the Earth. Mountains lose their ice, seas claim the land, forests burn or migrate, and deserts expand. These changes challenge how—and where—humans live.
Understanding how climate change reshapes global landscapes is the first step toward protecting what remains and adapting wisely. The planet is changing—now the responsibility lies with us to decide how much, how fast, and at what cost.


