🌍 Analyzing the Latest Trends in Global Trade (2025–2026)

According to recent assessments by World Trade Organization and UNCTAD, global trade in 2025 remains resilient — but uneven, fragmented, and more strategic than ever before.
📈 1. Global Trade Growth: Strong but Unequal
Despite economic uncertainties, global trade value has crossed USD 35 trillion, marking one of the highest levels in history.
Key Drivers of Growth
Strong recovery in services trade (tourism, IT, finance)
Rising demand for technology, electronics, and energy products
Expansion of South-South trade (trade among developing countries)
However, growth is not evenly distributed. Advanced economies are growing slowly, while emerging markets in Asia, Africa, and Latin America are becoming major trade engines.
🔎 Insight: Trade growth today is less about volume and more about strategic positioning and diversification.
🔄 2. Shifting Supply Chains: From Efficiency to Resilience

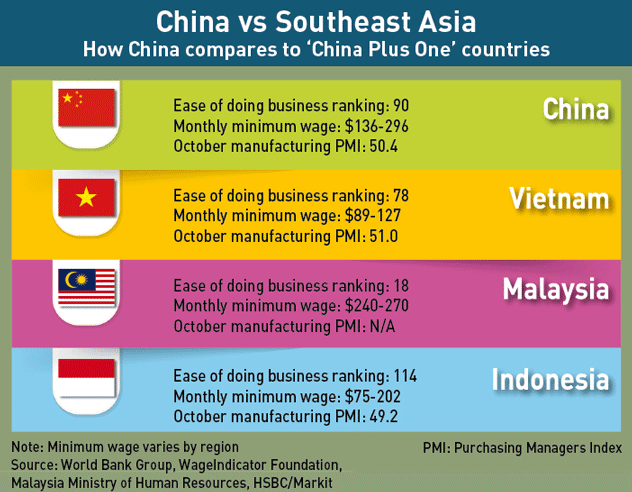
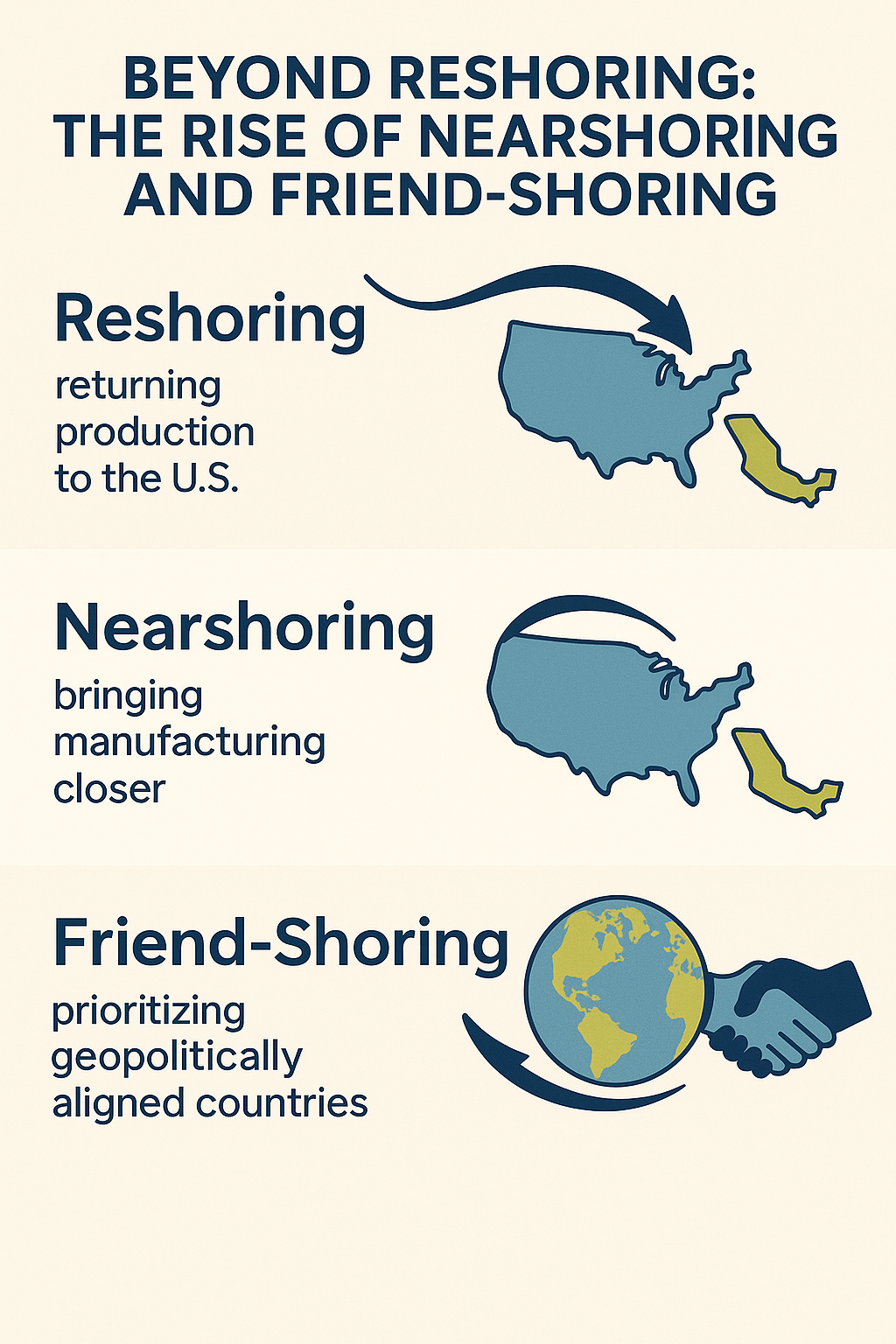
The old model of “lowest-cost global sourcing” is being replaced by risk-aware supply chains.
Major Supply Chain Trends
China+1 strategy: Companies reduce over-dependence on China by adding suppliers in Vietnam, India, Mexico, and Indonesia.
Nearshoring & friend-shoring: Production moves closer to consumer markets or allied countries.
Digital supply chains: Use of AI, blockchain, and real-time tracking.
Countries benefiting from this shift include India, Vietnam, Mexico, Poland, and Bangladesh.
🛃 3. Trade Policy: Return of Protectionism
Trade liberalization is slowing. Governments are increasingly using tariffs, subsidies, and industrial policies to protect domestic industries.
Key Policy Trends
Higher tariffs on steel, EVs, agriculture, and semiconductors
Strategic subsidies for clean energy and domestic manufacturing
Export controls on sensitive technologies
The World Trade Organization reports that trade-restrictive measures now affect over 10% of global merchandise trade, the highest level in decades.
⚠️ Result: More fragmented global trade, divided into regional and geopolitical blocs.
💻 4. Digital Trade & Services: The Fastest-Growing Segment



Digital trade has become the backbone of modern globalization.
What’s Growing Fast?
Cross-border e-commerce
IT services, software, cloud computing
Online education, freelancing, and digital content
FinTech and digital payments
Countries like India and the Philippines are global leaders in IT and business-process exports, while the US, EU, and China dominate digital platforms.
💡 Digital trade reduces dependence on physical logistics and offers huge opportunities for developing economies.
🌱 5. Sustainability & Green Trade
Environmental concerns are now shaping trade policy.
Green Trade Trends
Carbon border taxes (e.g., EU’s CBAM)
Demand for renewable energy equipment
Sustainable sourcing and ESG compliance
Growth in trade of electric vehicles and batteries
Firms that fail to meet environmental and labor standards risk losing market access.
🌍 Trade competitiveness today depends not only on price — but on carbon footprint and ethics.
🌐 6. Regional Trade & South-South Cooperation
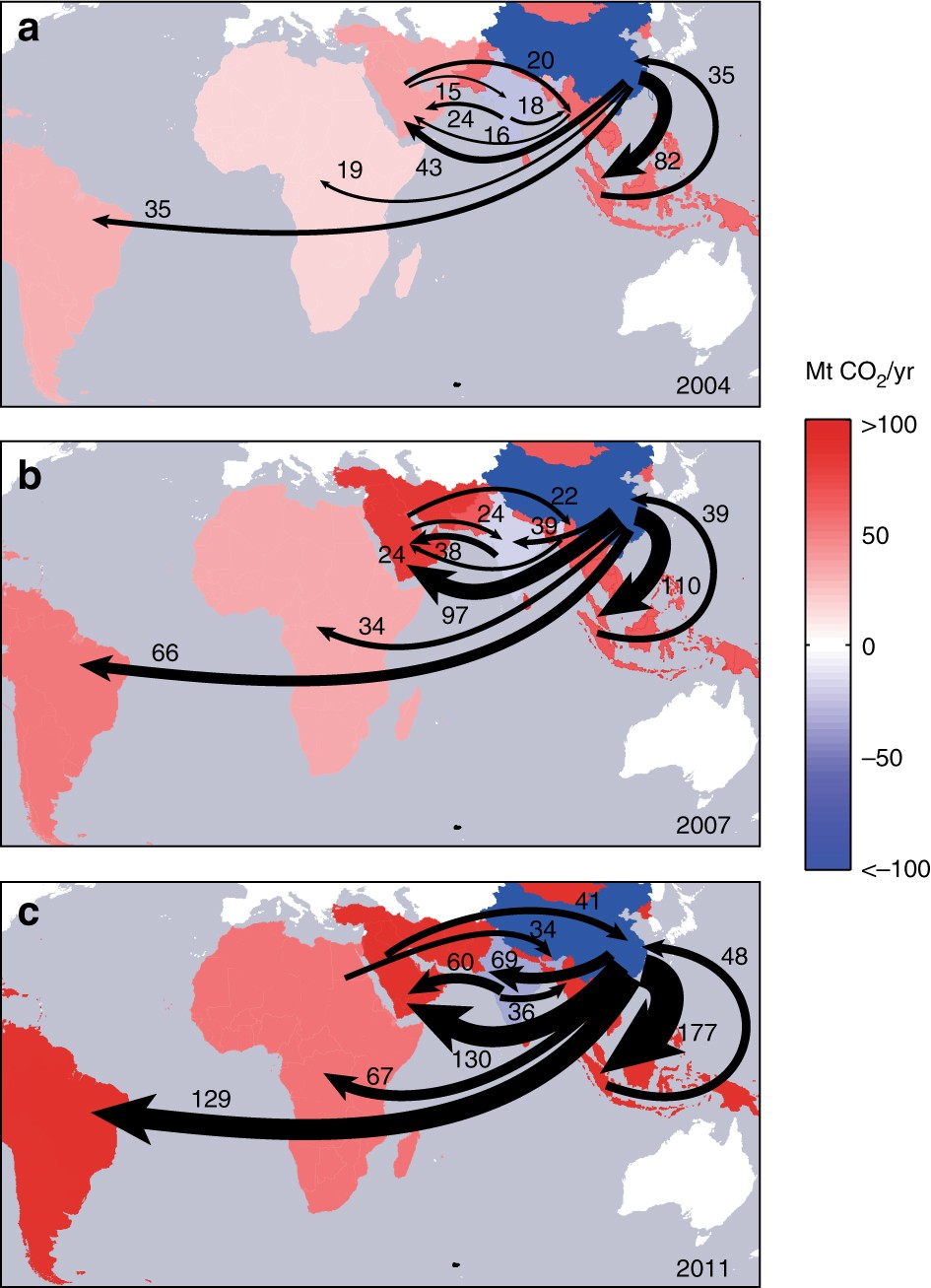
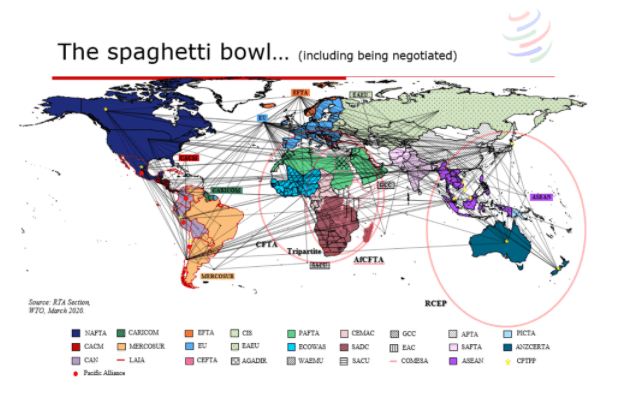

Regional trade agreements are reshaping global flows.
Notable Developments
Expansion of ASEAN intra-trade
Growth of African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA)
Strengthening ties among BRICS countries
Reduced dependence on traditional Western markets
This marks a power shift in global trade, with developing regions playing a larger role.
📊 7. Sector-Wise Trade Trends
| Sector | Trend |
|---|---|
| Technology | Strong growth (chips, AI hardware) |
| Energy | Shift from fossil fuels to renewables |
| Agriculture | Trade disruptions due to climate & policy |
| Manufacturing | Regionalization and automation |
| Services | Fastest growth sector |
🧩 8. Key Challenges Ahead
Despite positive momentum, global trade faces serious challenges:
🌐 Geopolitical conflicts
🛃 Policy unpredictability
🚢 Logistics disruptions
🌱 Climate risks
🤖 Digital divide between nations
These challenges require cooperation, reform, and innovation.
🔮 9. Future Outlook (2026 and Beyond)
Experts expect:
Moderate but stable trade growth
Greater regionalization
More digital and green trade
Increased role of emerging economies
Stronger link between trade and national security
Global trade is not declining — it is transforming.
✅ Conclusion
Global trade in 2025–2026 is defined by adaptation rather than expansion. Businesses and countries that succeed will be those that:
Diversify markets and suppliers
Embrace digital trade
Invest in sustainability
Stay agile amid policy shifts
Understanding these trends is essential for anyone involved in economics, business, education, or policy-making.

